Gas Mixture in CO₂ Laser Tube
The Gas Mixture is the active medium inside a CO₂ laser tube that makes laser generation possible. It is a carefully balanced blend of gases sealed within the discharge tube, and its composition directly determines the power, efficiency, and stability of the laser. Unlike solid-state or fiber lasers, the CO₂ laser relies on the excitation of gas molecules to produce infrared laser light, making the gas mixture one of the most vital components.
Composition of the Gas Mixture
The typical CO₂ laser gas mixture contains:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) – Around 8–20%
The primary lasing medium.
Excited CO₂ molecules emit infrared photons at 10.6 μm wavelength (sometimes at 9.6 μm).
- Nitrogen (N₂) – Around 10–20%
Plays the role of an energy transfer agent.
Nitrogen molecules are easily excited by electrical discharge and then transfer their energy to CO₂ molecules.
- Helium (He) – Around 60–80%
Acts as a cooling and balancing gas.
Helps remove excess heat from the gas mixture.
Increases efficiency by de-exciting lower-energy CO₂ states, keeping the laser action stable.
- Optional Additives (small amounts)
Hydrogen (H₂) – Helps increase tube lifespan by reducing impurities.
Xenon (Xe) – Improves discharge stability.
Water Vapor – Sometimes used to reduce arcing and extend tube life.
Functions of the Gas Mixture
- Laser Generation – CO₂ molecules are excited and release infrared photons when returning to a lower energy state.
- Energy Transfer – Nitrogen provides energy to CO₂ molecules for more efficient excitation.
- Thermal Management – Helium dissipates heat and ensures smooth operation.
- Stability – The balanced gas mix prevents electrical instability and maintains consistent laser output.
- Beam Quality – The ratio of gases affects beam sharpness, intensity, and lifespan of the tube.
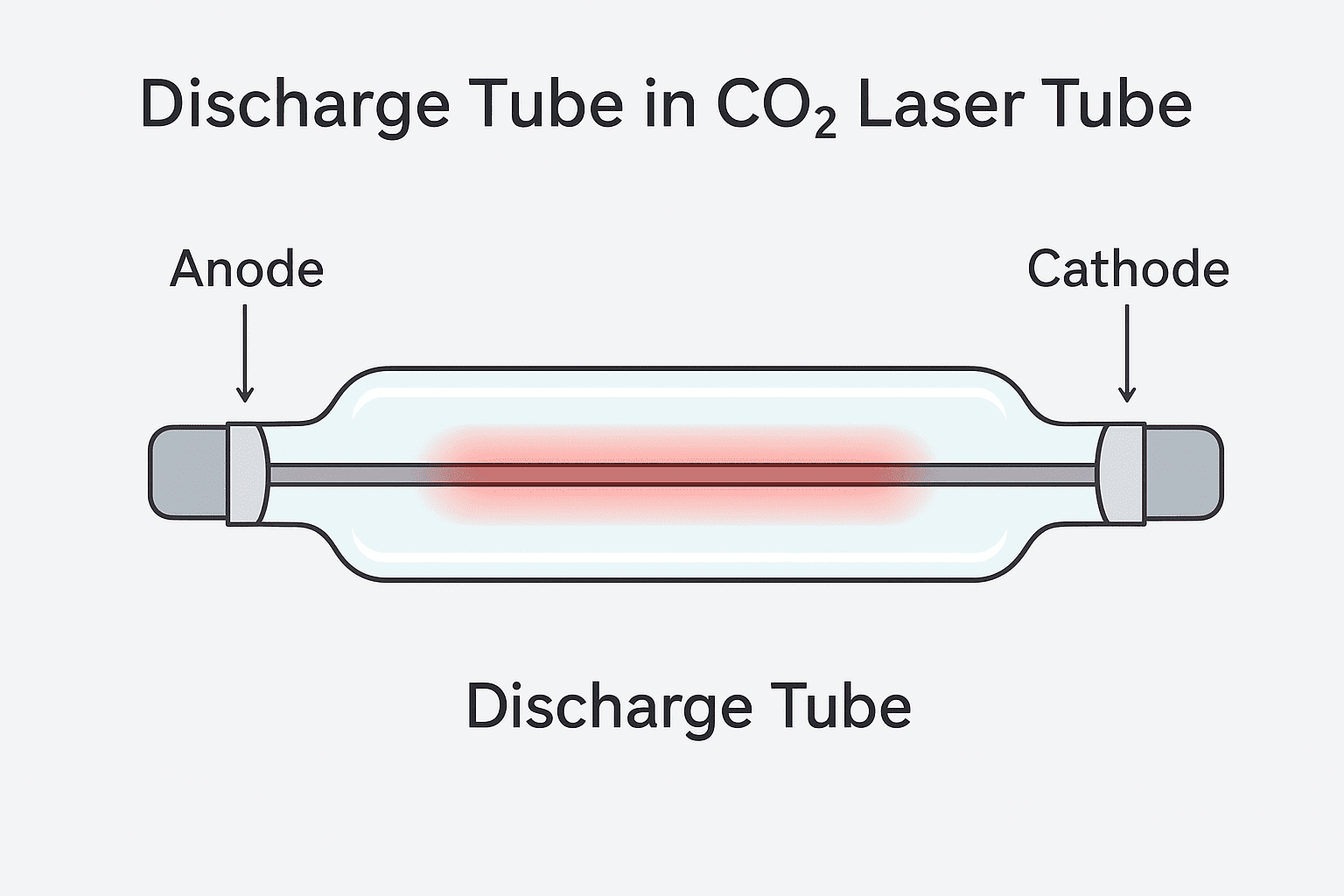
How the Gas Mixture Works in the Laser Tube
- Electrical Discharge excites nitrogen molecules in the discharge tube.
- Nitrogen Transfers Energy to CO₂ molecules, pushing them to a higher vibrational energy state.
- Photon Emission occurs when CO₂ molecules drop back to a lower state, releasing infrared light.
- Amplification happens as photons bounce between mirrors, stimulating more emissions.
- Laser Output is released through the output coupler, producing the final laser beam.
Features of a Good Gas Mixture
- Purity: Contaminants can reduce tube life.
- Correct Ratio: Ensures maximum efficiency and stable operation.
- Sealed for Longevity: Proper sealing maintains gas pressure for thousands of hours.
- Optimized Cooling: Adequate helium balance prevents overheating.


Leave A Comment