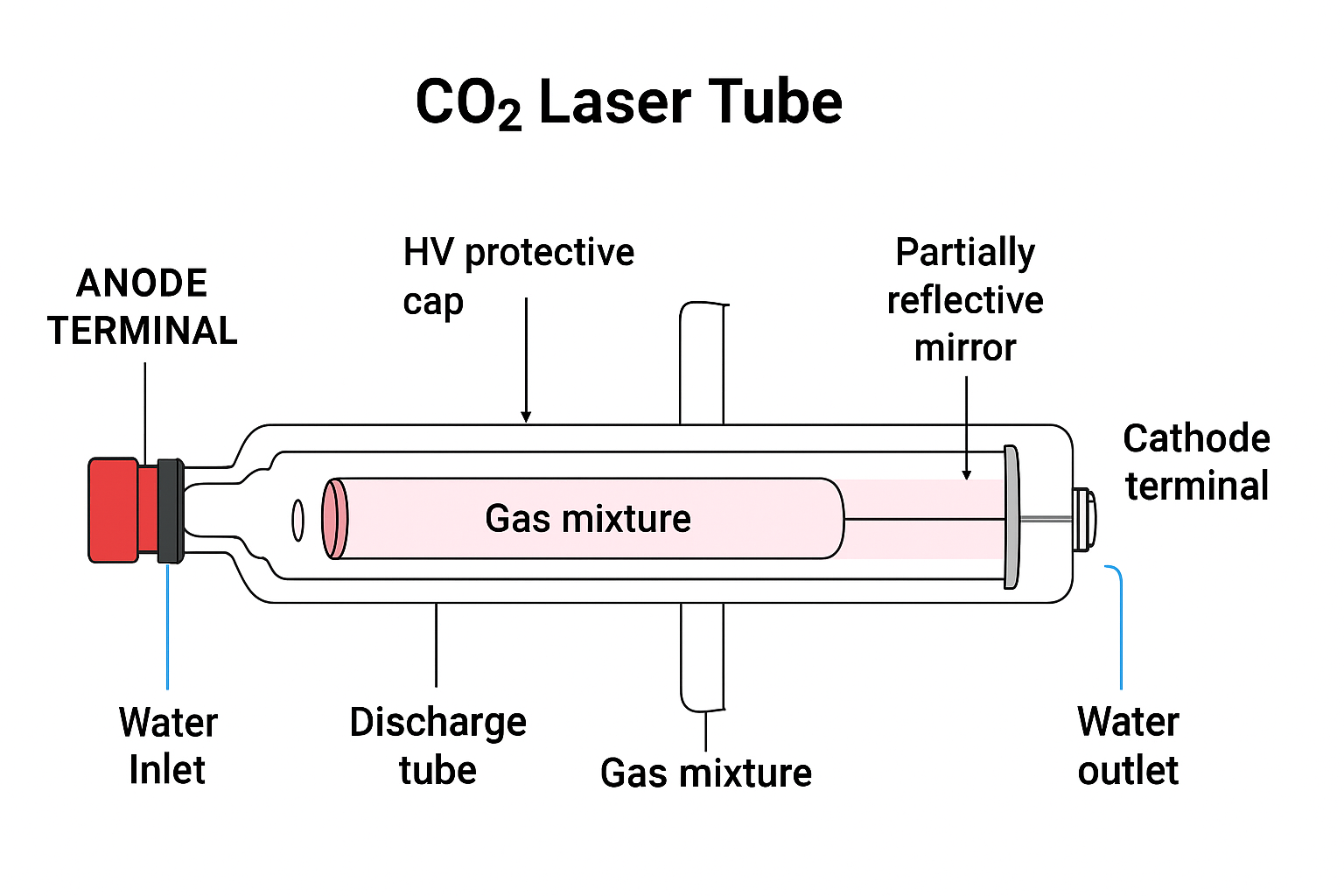
What is a CO₂ Laser Tube?
A CO₂ laser tube is the heart of a laser cutting and engraving machine. It is a long, sealed glass tube filled with a carefully balanced gas mixture of Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Nitrogen (N₂), and Helium (He). When connected to a high-voltage power supply, the laser tube creates an electrical discharge that excites these gases, leading to the generation of a powerful laser beam.
Table of Contents
How Does It Work?
A CO₂ laser tube is the heart of a laser cutting and engraving machine. It is a long, sealed glass tube filled with a carefully balanced gas mixture of Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Nitrogen (N₂), and Helium (He). When connected to a high-voltage power supply, the laser tube creates an electrical discharge that excites these gases, leading to the generation of a powerful laser beam.
The working principle can be broken down into the following steps:
- Electrical Discharge – High voltage is applied across the anode and cathode terminals, producing a discharge inside the tube.
- Gas Excitation – Nitrogen molecules get energized first, transferring their energy to CO₂ molecules.
- Photon Emission – Excited CO₂ molecules release energy in the form of infrared light photons when they return to their stable state.
- Optical Resonance – The photons bounce back and forth between two mirrors: one fully reflective and one partially reflective. This amplifies the light into a powerful laser beam.
- Laser Output – The partially reflective mirror allows the beam to exit the tube in a concentrated form.
- Cooling Process – To prevent overheating, cooling water circulates through the outer cooling jacket via inlet and outlet ports.
The result is a high-intensity infrared laser beam with a wavelength of 10.6 µm, which is ideal for cutting, engraving, and marking materials such as wood, acrylic, MDF, leather, paper, and even certain fabrics.
What are the Main Parts of a CO₂ Laser Tube?
A CO₂ laser tube is made up of several critical components, each with a specific function in generating the laser beam:
- Anode Terminal – The positive electrode that receives the high voltage to start the discharge.
- Cathode Terminal – The negative electrode that completes the electrical circuit.
- Discharge Tube – The inner tube filled with CO₂, N₂, and He gases, where the actual excitation happens.
- Gas Mixture –
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Responsible for producing the infrared laser light.
- Nitrogen (N₂): Helps excite CO₂ molecules by transferring energy.
- Helium (He): Helps in cooling the gas mixture and increasing efficiency.
- Outer Cooling Jacket – A larger glass tube surrounding the discharge tube that allows water circulation.
- Water Inlet and Outlet – Ports for water cooling to maintain a stable temperature and prevent damage.
- Fully Reflective Mirror – Positioned at one end of the tube, it reflects 100% of the photons back into the discharge tube.
- Partially Reflective Mirror – At the opposite end, it lets out a portion of the amplified light as the actual laser beam.
- Protective HV Cap – A safety cover around the high-voltage connection to prevent electric shocks and arcing.
Together, these parts ensure that the CO₂ laser tube produces a powerful, stable, and precise laser beam suitable for industrial and DIY applications.
Why is the CO₂ Laser Tube Important?
The CO₂ laser tube is what makes a laser cutting machine functional. Without it, the machine would not be able to generate the powerful light required to cut or engrave materials. A well-functioning tube ensures:
- High cutting precision
- Smooth engraving quality
- Long operational life of the machine
- Consistent performance
Regular maintenance, correct water cooling, and proper power supply usage significantly extend the lifespan of the tube.

Leave A Comment